Load Cells Driving Intelligent Farming Solutions
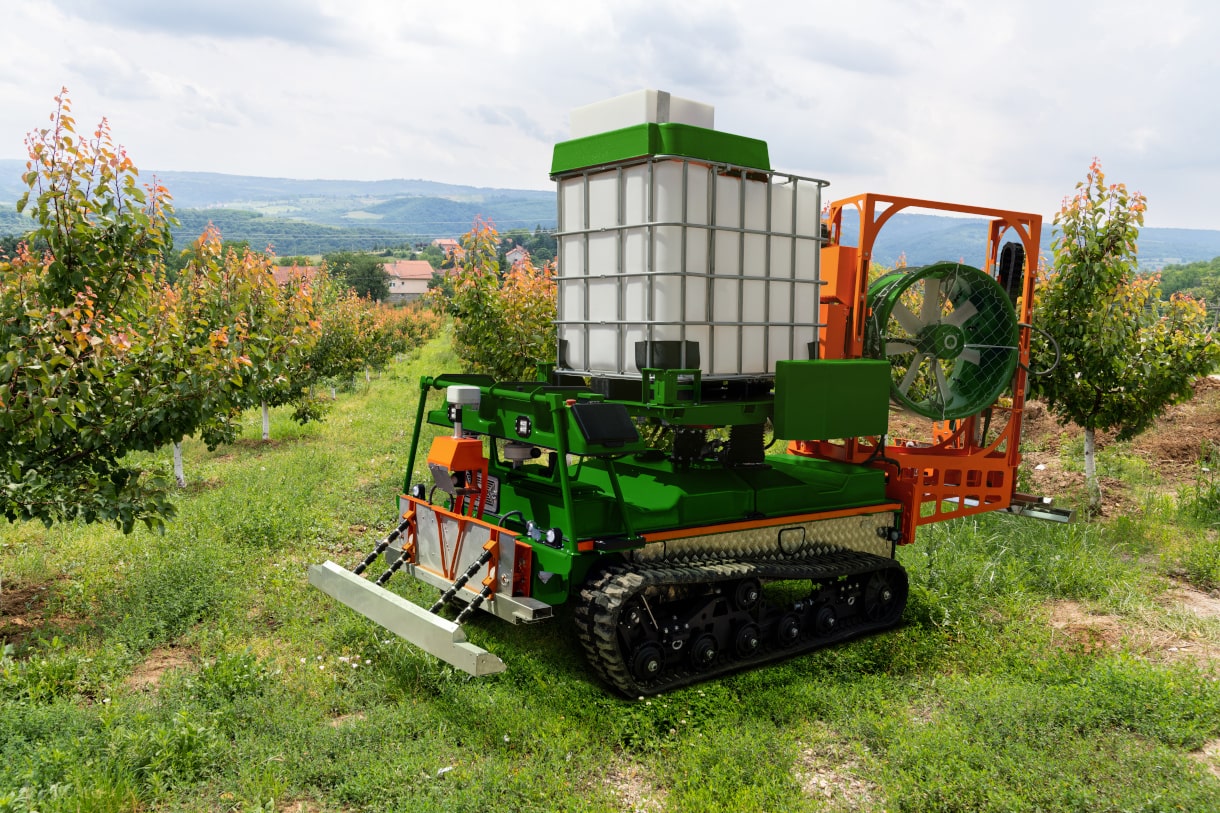

Innovations throughout history have propelled agribusiness to harvest more with greater efficiency. Early Babylonians created a wind-powered machine and a seed drill. In China, innovations included the iron plow and rotary winnowing machine. Innovations continue in the effort to meet the food demands of the ever-growing world population.
Today, the concept of smart farming is transforming traditional farming methods. Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in agriculture opens new avenues for agribusiness management to practice data-driven farming with higher efficiency, safety, and risk management.
Load cells are among the core precision sensors for intelligent farming. They offer precise force measurement capabilities, compatibility with IoT network infrastructures, and the durability to work in harsh environments.
Here’s a look at how load-cell integrations are creating new opportunities for agriculture businesses.
How Load Cells Enhance Agribusiness Management
Load cells provide accurate weighing data that drives decision-making, enabling precise control of factors such as fertilizer, irrigation, and feed management, while also enhancing tractor performance and optimizing equipment functions through force and weight measurement.
Weighing Data that Drives Decisions
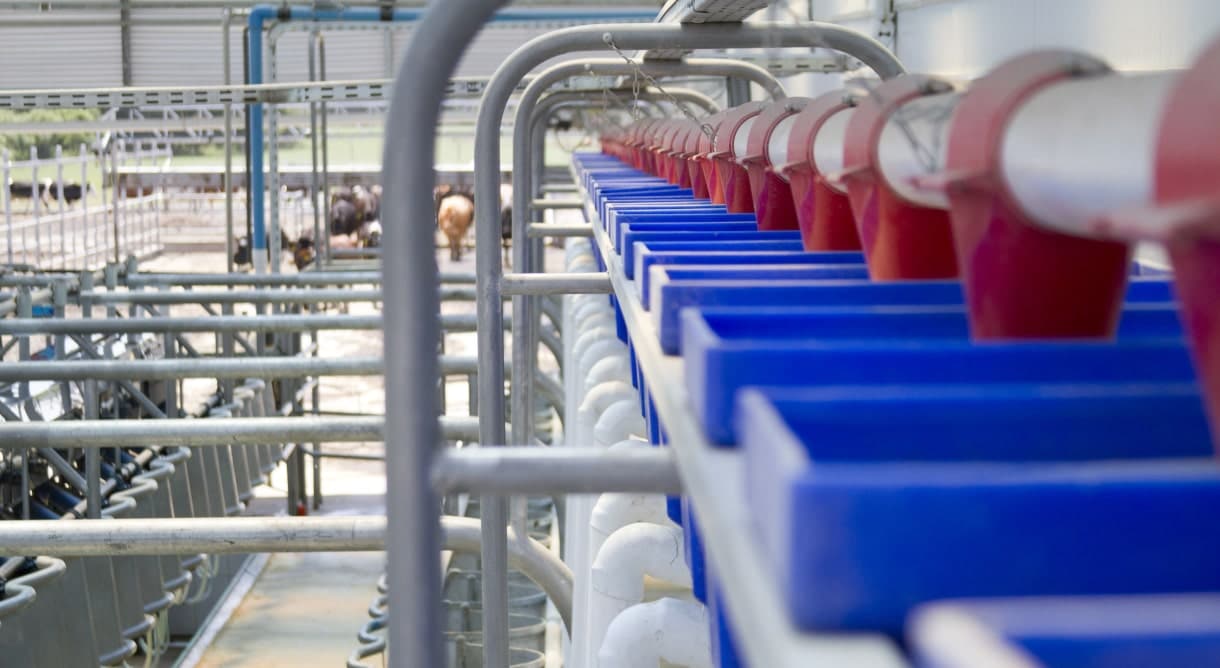 Aside from optimal climate conditions, maximizing crop quality and yield involves achieving the right balance of factors, primarily fertilizer, irrigation, weed control, and pest management. Precise control of these variables using accurate data supports efficient farming. Weighing applications powered by force transducers allow farmers to measure what goes in accurately and comes out of their lands.
Aside from optimal climate conditions, maximizing crop quality and yield involves achieving the right balance of factors, primarily fertilizer, irrigation, weed control, and pest management. Precise control of these variables using accurate data supports efficient farming. Weighing applications powered by force transducers allow farmers to measure what goes in accurately and comes out of their lands.
- Crop yields. Silo and hopper weighing systems for grain stock control, weighbridges for outbound produce, and onboard weighing units for day-to-day operations provide the information for accurate harvest reports. Load cells also help farm managers balance inventory across multiple storage units.
- Livestock and poultry feed management. A balanced diet is essential for farm animals’ health. Even slight deviations put livestock at risk. Advanced feed management tools help farmers precisely weigh and mix animal feeds to ensure they get the nutrition they need.
- Livestock weighing. Livestock weigh scales allow agribusiness management to track animal growth, identify diseased animals, and forecast meat production.
- Tank weighing. Tank weighing systems let farmers manage inventory and application rates in the field to know if they are running short on supply and allow them to plan accordingly.
The Tractor Reimagined
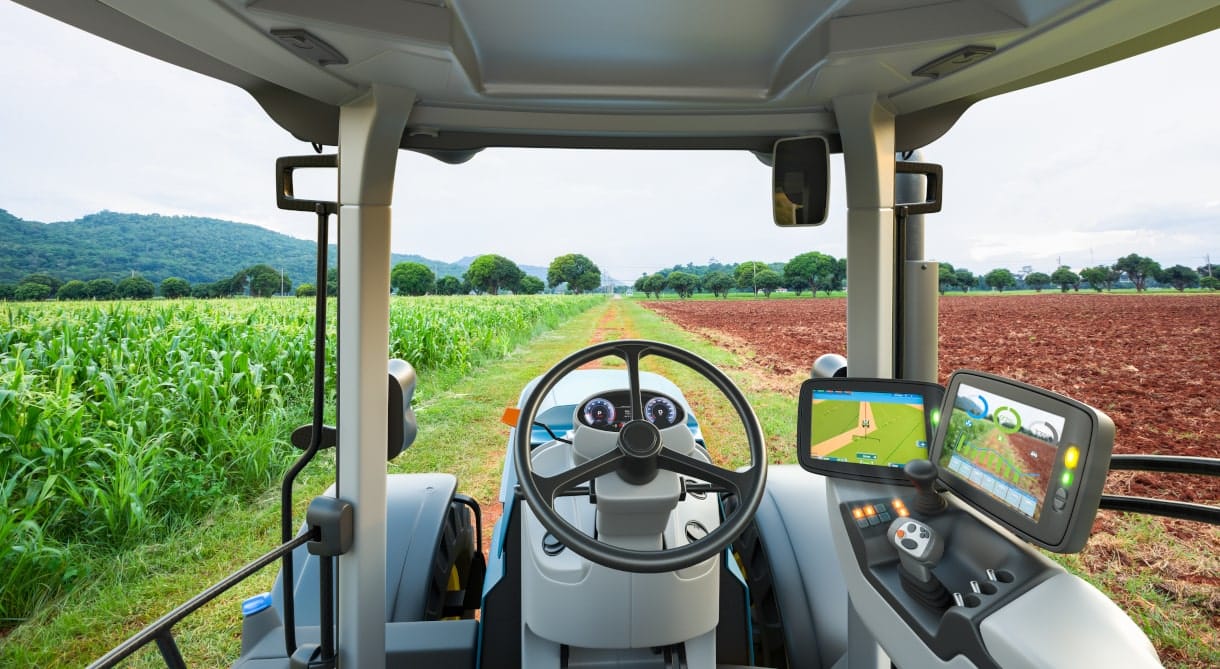 Load cells are pivotal in ensuring modern farm tractors’ accuracy, safety, and efficiency. Technology-centric tractors, harvesters, and implements rely on force sensors that drive integrated systems that support more accurate plowing, harvesting, and equipment life. Load cells are essential control system components that make this equipment accurate and safe.
Load cells are pivotal in ensuring modern farm tractors’ accuracy, safety, and efficiency. Technology-centric tractors, harvesters, and implements rely on force sensors that drive integrated systems that support more accurate plowing, harvesting, and equipment life. Load cells are essential control system components that make this equipment accurate and safe.
- Tractor draft control. Soil hardness is not uniform across fields, putting extra strain on tractors when plowing harder sections. Conversely, on softer ground, a plow may cut too deeply. Controlling plow depth through draft control extends tractor life, optimizes plow depth, and supports fuel efficiency. Tractor draft control technology uses load cells to sense ground resistance and adjusts the plow depth to maintain a uniform load on the tractor.
- Power measurement. Intelligent force monitoring systems help regulate tractor power take-off systems with force and torque measurement and brake power testing. System data supports the efficient and safe operation of tractors and powered attachments.
- Lifts. Factory farms today manage pallets and bins of harvested crops using mobile industrial lift systems on tractors or skid steers that include weighing systems and safety features using load cells.
- Seeding and fertilizing equipment. Incorporating load cells in equipment like seeders and manure spreaders lets equipment operators monitor mass flow rate and tank weight. With variable-rate application systems, seeding and fertilizing equipment can adjust the application rates based on the specific needs of different areas within a field.
- Hay baler control. Hay bale quality largely depends on weight, size, and density. Baler control systems use load cell force measurements to optimize these qualities and maximize profits.
Load cells from companies like Transcell provide the backbone for force and weight measurement for farming equipment. The force measurement devices produce electrical signals that integrate with precision display indicators, wireless communication devices, data-capturing systems, and more. They support complex functions using PLC, PAC, and IoT platforms.
Putting the ‘Smart’ in Smart Farming
The growing integration of IoT in agriculture supports farmers in unprecedented ways, helping them focus more on productivity. They can use smart equipment so they can work smarter, not harder.
Load Cell Applications for Agribusiness
- Data visualization: Real-time sensors produce data for easy-to-read data visualizations that help farmers make informed decisions. Farm managers can customize their data dashboards to focus on specific goals like profitability, preventive maintenance, and health monitoring.
- Real-time alerts: In today’s massive farms, detecting issues like equipment failure or crop diseases on time is difficult. Through sensor placement at critical information nodes, real-time web-based monitoring systems can make farmers’ lives easy by issuing real-time alerts on mobile apps, automatic safety stops, and data-driven maintenance scheduling.
- Data analytics: Data logging and analytics helps farmers make better decisions with information revealing hidden production patterns. Transferring load-cell information into a database can be used to prepare yield forecasts correlated with historical and projected climatic conditions.
- Integrated systems: Farm data serves as the input to PLC-based integrated systems that trigger operations like greenhouse environment control, air conditioning and ventilation in livestock barns, hydroponics, feeding systems, and more.
- OEM communication systems: The growing adaptation of agriculture-compatible IoT tech by trusted OEM communication system providers greatly enhance agribusiness opportunities. With even small- to medium-sized farmers getting access to standard industrial communication protocols, IoT is driving change in its true sense.
Agriculture Case Studies Featuring Load Cells
With the agriculture industry in the midst of a digital transformation, the fusion of load cells and IoT is a hot topic of research. R&D teams around the world are developing innovative new solutions that incorporate these technologies.
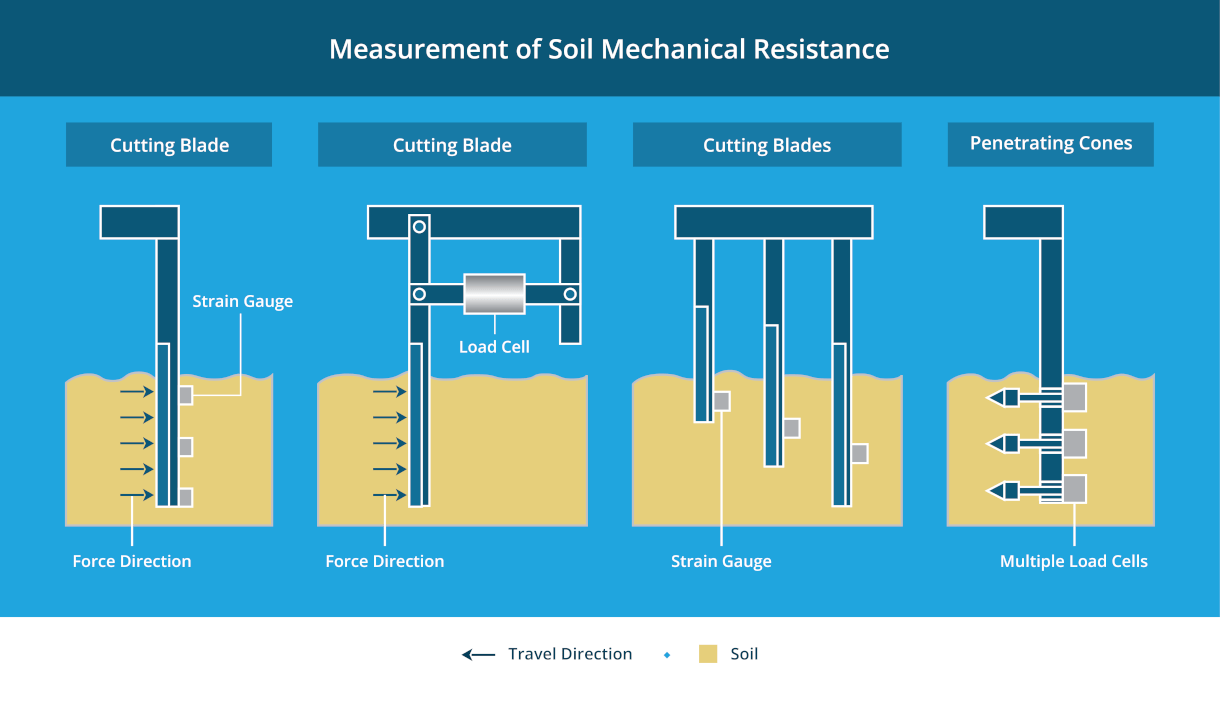
A Slovak University of Agriculture research team designed a Soil Resistance Force Sensor (SRFS) using load cells integrated with real-time data acquisition technology. Mounted on the tractor’s plow, their device relays soil health status to farmers on the go. This information helps farmers make data-driven decisions about soil preparation and tractor maintenance.
The Wageningen Agricultural University developed a dynamic weighing method to control the mass flow rate of fertilizer spreaders. The device can be calibrated for different fertilizers and crops.
Researchers at the Süleyman Demirel University used load cells with computer vision algorithms to develop an apple sorting mechanism. Their smart farming solution sorted apples based on color, size, and weight with up to 79% accuracy at a rate of 432,000 apples in an eight-hour shift.
The Future – Moving Towards Smarter Farming
The agriculture industry is evolving quickly, but is still far from full-scale digitization. The role of smart farming technologies is continuously growing as more impactful products enter the market.
- Autonomous farming: Once a dream, autonomous farming is now a very real possibility. The World Economic Forum predicts the autonomous farming industry to grow to $95 billion by 2027. Load cells are a critical component of many autonomous farming innovations. With technologies such as GPS, long-range connectivity, and machine vision, self-driving tractors and autonomous seeders are just around the corner.
- Irrigation management: Looking to a future with water scarcity, Oregon State University researchers Dalyn M McCauely and Lloyd L. Nackley developed a load-cell-based lysimeter as a proof of concept that could support better agricultural water management systems. The device directly measures evapotranspiration by a change in the mass of containerized crops.
Harvesting Efficiency and Profitability
Smart farming is playing a major role in helping agribusinesses take on the sustainability challenges of the future. Reliable and efficient products like load cells, integrated with IoT and wireless systems, has spearheaded a remarkable evolution in agricultural methodologies.
Contact Transcell to discuss customized solutions for your OEM agriculture equipment.
